
What is HIV
HIV (human immunodeficiency virus) is a virus that attacks the body’s immune system. If HIV is not treated, it can lead to AIDS (acquired immunodeficiency syndrome).
There is currently no effective cure. Once people get HIV, they have it for life.
But with proper medical care, HIV can be controlled. People with HIV who get effective HIV treatment can live long, healthy lives and protect their partners.
HIV Transmission
The majority of HIV transmissions occur via unprotected anal or vaginal intercourse, or by sharing needles, syringes, or other paraphernalia used in drug injection, such as cookers. However, there are effective strategies available to reduce the risk of HIV infection. More info in CDC
How do I know if I have HIV?
The only way to know if you have HIV is to get tested. Knowing your HIV status helps you make healthy decisions to prevent getting or transmitting HIV.

Are there symptoms?
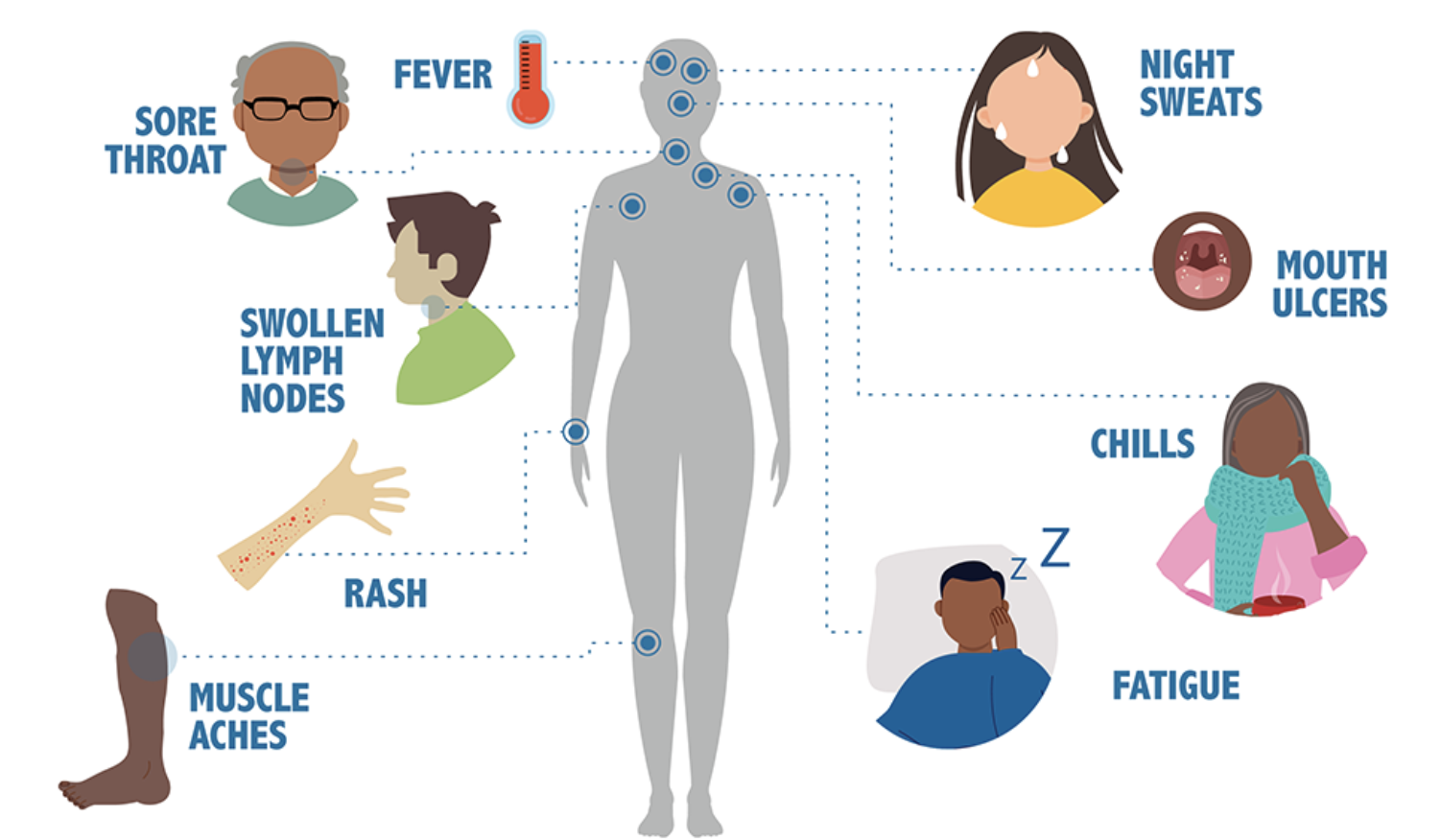
The symptoms of HIV can vary from person to person, but the initial infection can produce a flu-like illness within two to four weeks after the virus enters the body. This is known as acute retroviral syndrome (ARS) or primary HIV infection, and the symptoms can include:
- Fever
- Chills
- Rash
- Night sweats
- Muscle aches
- Sore throat
- Fatigue
- Swollen lymph nodes
- Mouth ulcers
Reference: Reference